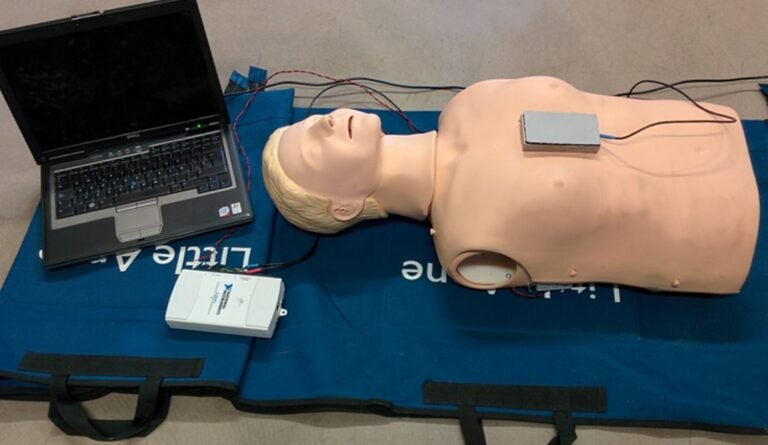
Chest compressions are an essential part of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and can greatly improve the chances of survival for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. However, performing chest compressions correctly can be challenging, especially in high-stress situations. This is where chest compression feedback devices come into play.
What is a Chest Compression Feedback Device?
A chest compression feedback device is a tool used to monitor and provide real-time feedback on the quality of chest compressions during CPR. It typically consists of sensors that are placed on the patient’s chest and a display screen or audio cues that guide the rescuer in performing compressions at the correct depth, rate, and rhythm.
What Does it Monitor?
A chest compression feedback device monitors several key factors during CPR, including:
- Compression depth: The device measures the depth of each compression and provides feedback if it is too shallow or too deep. Studies have shown that compressions should be at least 2 inches (5 cm) deep to effectively pump blood to the heart and brain.
- Compression rate: The device tracks the number of compressions per minute and alerts the rescuer if they are going too fast or too slow. The American Heart Association recommends a compression rate of 100-120 per minute.
- Hand position: Proper hand placement is crucial for effective chest compressions. A feedback device can detect if the hands are in the correct position and provide guidance for readjustment if needed.
- Compression pauses: Interruptions in chest compressions can significantly decrease the chances of survival. A feedback device monitors compression pauses and provides prompts to keep a steady rhythm.
Why is it Important?
Using a chest compression feedback device during CPR has several benefits:
- Improved Quality: By providing real-time feedback, these devices help rescuers perform high-quality chest compressions consistently, which results in better blood flow to vital organs.
- Decreased Fatigue: CPR is physically demanding, and fatigue can quickly set in for the rescuer. A feedback device helps maintain a consistent compression depth and rate, reducing fatigue and ensuring effective compressions throughout the rescue.
- Training Tool: Chest compression feedback devices are also useful for training purposes. They can provide visual or auditory cues to guide new rescuers on proper technique and help experienced rescuers fine-tune their skills.
How to Use a Chest Compression Feedback Device?
Using a chest compression feedback device is relatively straightforward. The device is typically placed on the patient’s chest, over the sternum where compressions are normally performed. Once in place, the device begins to measure and record data as soon as chest compressions start. Real-time feedback is provided, either visually through a screen or audibly through headphones or speakers, allowing the rescuer to adjust their technique as necessary.
Limitations and Considerations
While chest compression feedback devices are extremely beneficial, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, these devices are tools to assist rescuers, not to replace proper CPR training. They should be used in conjunction with, not as a substitute for, formal CPR education and practice. Second, while feedback devices can help maintain effective compression depth and rate, they can’t measure other important aspects of CPR such as airway management and ventilation. Lastly, the devices may not perform optimally in all situations, like in moving vehicles or when used on surfaces that aren’t firm. Despite these limitations, the benefits of using a chest compression feedback device in both training and real-life rescue situations are significant and could potentially save lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a chest compression feedback device serves as a highly beneficial tool in the realm of cardiac arrest management and CPR training. Monitoring key elements such as compression depth, rate, hand positioning, and pauses, allows for better adherence to recommended guidelines, enhancing the effectiveness of chest compressions and ultimately the patient’s chance of survival. Regardless of the limitations and considerations, the role of a chest compression feedback device is undeniably crucial, bridging the gap between theory and practice, and ensuring that lifesaving chest compressions are delivered correctly and efficiently. The incorporation of such devices into CPR training and emergency response scenarios could significantly improve the outcomes of cardiac arrest patients. So, it is important for healthcare providers and rescuers to stay updated on the latest advancements in chest compression feedback devices and incorporate them into their practice. Together, we can work towards better outcomes for those experiencing cardiac arrest.
Visit to read more articles: Etho Zen